'Nine-primaried oscines'
John Harshman

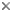
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxDiscussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
The nine-primaried oscines form a strongly supported group (Klicka et al. 2000; Ericson and Johansson 2003; Barker et al. 2004), including the families Fringillidae (finches), Emberizidae (buntings and New World sparrows), Icteridae (New World blackbirds), Parulidae (New World warblers), Thraupidae (tanagers), and Cardinalidae (grosbeaks). Fringillidae is the sister of the others (Klicka et al. 2000; Yuri and Mindell 2002; Ericson and Johansson 2003; Barker 2004). Two genera previously considered emberizids, Calcarius (longspurs) and Plectrophenax (snow buntings) are sister taxa of each other and together the sister of the remaining nine-primaried oscines (Klicka et al. 2000; Yuri and Mindell 2002; Ericson and Johansson 2003). Relationships among the remaining five families are contentious. Of analyses with representatives of all five families, most unite Cardinalidae and Thraupidae (Bledsoe 1988; Barker et al. 2002, 2004; Yuri and Mindell 2002), though two (Sibley and Ahlquist 1990; Harshman 1994; Klicka et al. 2000) do not. Again, most unite Icteridae and Parulidae (Bledsoe 1988; Barker et al. 2002, 2004), though two (Klicka et al. 2000; Yuri and Mindell 2002) do not. But support for the minority arrangements are weak. The position of Emberizidae is unclear; Barker et al. (2002, 2004) have strong support for relationship to the cardinalid-thraupid clade; Bledsoe (1988) found a relationship to the parulid-icterid clade; Yuri and Mindell (2002) and Klicka et al. (2000), though failing to find the parulid-icterid clade, did find a clade consisting of Emberizidae, Icteridae, and Parulidae. For the present, relationships of Emberizidae are best treated as unresolved.
References
Barker, F. K. 2004. Monophyly and relationships of wrens (Aves: Troglodytidae): A congruence analysis of heterogeneous mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequence data. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 31:486-504.
Barker, F. K., G. F. Barrowclough, and J. G. Groth. 2002. A phylogenetic hypothesis for passerine birds; Taxonomic and biogeographic implications of an analysis of nuclear DNA sequence data. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 269:295-308.
Barker, F. K., A. Cibois, P. Schikler, J. Feinstein, and J. Cracraft. 2004. Phylogeny and diversification of the largest avian radiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:11040-11045.
Beresford, P., F. K. Barker, P. G. Ryan, and T. M. Crowe. 2005. African endemics span the tree of songbirds (Passeri): Molecular systematics of several evolutionary "enigmas". Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 272:849-858.
Bledsoe, A. H. 1987. DNA evolutionary rates in nine-primaried passerine birds. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4:559-571.
Ericson, P. G. P., U. S. Johansson, and T. J. Parsons. 2000. Major divisions in oscines revealed by insertions in the nuclear gene c-myc: A novel gene in avian phylogenetics. Auk 117:1069-1078.
Ericson, P. G. P., and U. S. Johansson. 2003. Phylogeny of Passerida (Aves: Passeriformes) based on nuclear and mitochondrial sequence data. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 29:126-138.
Fuchs, J., J. Fjeldså, R. C. K. Bowie, G. Voelker, and E. Pasquet. 2006. The African warbler genus Hyliota as a lost lineage in the oscine songbird tree: Molecular support for an African origin of the Passerida. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 39:186-197.
Harshman, J. 1994. Reweaving the Tapestry: What can we learn from Sibley and Ahlquist (1990)? Auk 111:377-388.
Harshman, J. 2007. Classification and phylogeny of birds. Pages 1-35 in Reproductive biology and phylogeny of birds (B. G. M. Jamieson, ed.). Science Publishers, Inc., Enfield, NH.
Klicka, J., K. P. Johnson, and S. M. Lanyon. 2000. New World nine-primaried oscine relationships: Constructing a mitochondrial DNA framework. Auk 117:321-336.
Sibley, C. G., and J. A. Ahlquist. 1990. Phylogeny and classification of birds, Yale U. Press, New Haven.
Sibley, C. G., and B. L. Monroe Jr. 1990. Distribution and taxonomy of birds of the world, Yale University Press, New Haven.
Yuri, T., and D. P. Mindell. 2002. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Fringillidae, "New World nine-primaried oscines" (Aves: Passeriformes). Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 23:229-243.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Passerina cyanea |
|---|---|
| Location | Desoto National Wildlife Refuge, Iowa, USA |
| Comments | Indigo Bunting |
| Creator | Dave Menke |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Source Collection | U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Online Digital Media Library |
| Scientific Name | Thlypopsis sordida |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Source | Saíra-canário |
| Source Collection | Flickr |
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs License - Version 2.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs License - Version 2.0.
|
| Copyright | © 2006 Antonio CBC Lopes |
| Scientific Name | Molothrus ater |
|---|---|
| Location | Lino Lakes, MN |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Identified By | Scott M. Lanyon |
| Sex | Male |
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© Scott Lanyon

|
About This Page
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to John Harshman at
Page copyright © 2006
 Page: Tree of Life
'Nine-primaried oscines'.
Authored by
John Harshman.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
'Nine-primaried oscines'.
Authored by
John Harshman.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 02 August 2006
- Content changed 02 August 2006
Citing this page:
Harshman, John. 2006. 'Nine-primaried oscines'. Version 02 August 2006 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/%27Nine-primaried_oscines%27/67287/2006.08.02 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/










 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site